참가에 관심있는 분들은 이훈희(E-mail: hunheelee_at_snu_dot_ac_kr)에게 메일로 문의바랍니다.
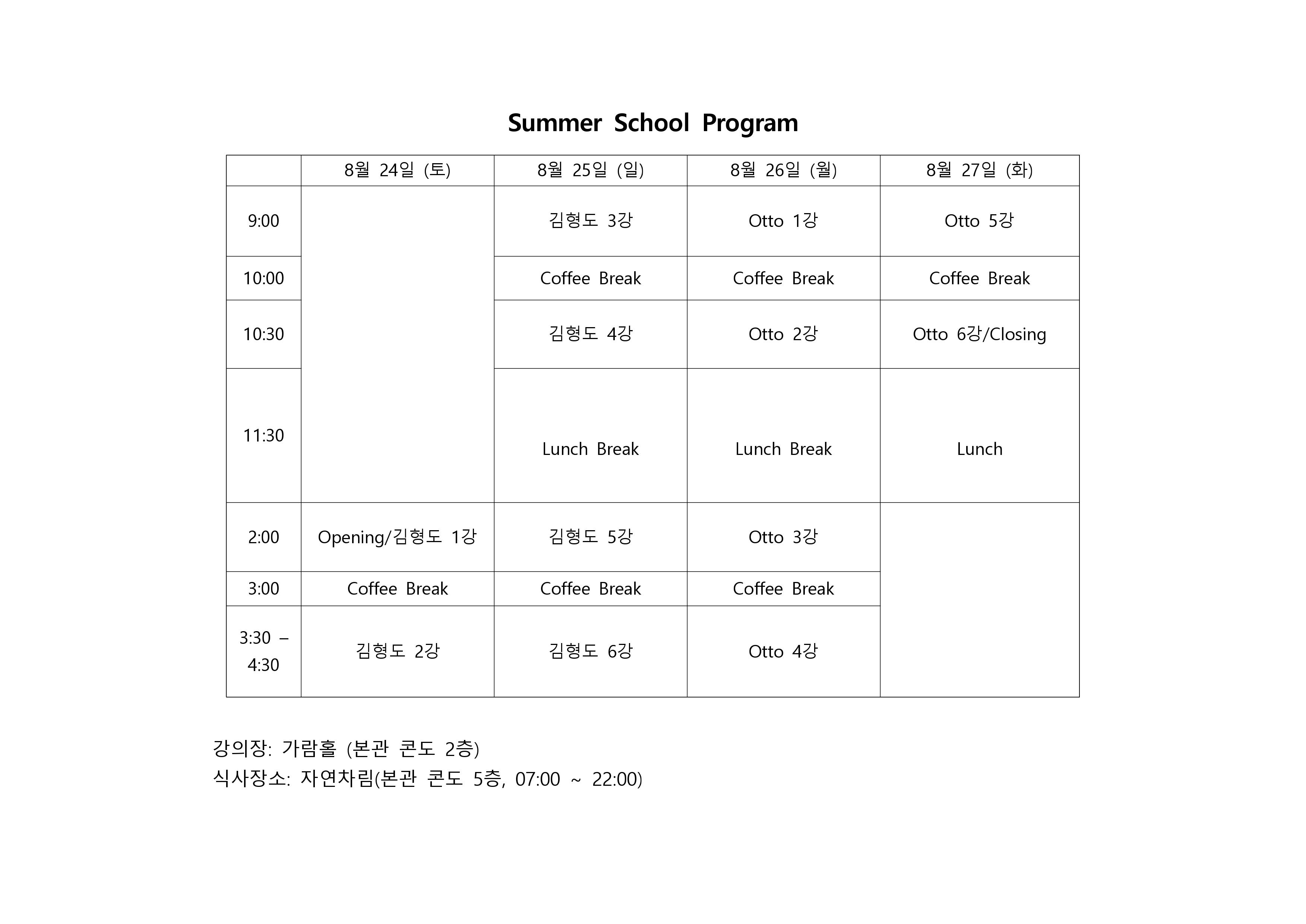
강연안내
Plan for the lectures:
Lec 1: From classical mechanics to quantum mechanics
· Netwon's 2nd law : F=ma
=> Lagrangian (Euler equation)
=> Hamiltonian (Legendre transformation)
=> Least action principle
=> Path integral
· Poisson bracket => Dirac bra-ket : canonical quantization => matrix mechanics
· Hamilton-Jacobi equation to Schr\"odinger equation => wave mechanics (representation using differential operator)
· Path integral (Lagrangian vs Hamiltonian)
Lec 2: Black body radiation
· Historical review of electromagnetism and thermodynamics
· Concept of perfect 'black body'
· UV catastrophe
· Planck's solution to the UV catastrophe problem
· Connection to Einstein's photoelectric effect
· Photon as a 'relativistic' particle
· Wave (electromagnetism) and particle (photon) duality
Lec 3. Symmetry and generators
· Noether theorem (classical) : conserved quantity associated to the symmetry of the system
· Space translation => momentum
Time translation => energy
Rotation => angular momentum
Lorentz rotation (rotation and boost) => angular momentum and spin
· Generator of the transformation : corresponds to the conserved quantity
Lie group of the transformation : associated Lie algebra of the generators
Lec 4. Harmonic oscillator
· Classical motion of harmonic oscillator and why it is so important
· Solution of Schrodinger equation with quantum mechanical harmonic oscillator
· Potential : eigenvalue and eigenstate
· Algebraic approach to the solution
=> advanced topic : coherent state (translation of the ladder operator eigenvalue)
Lec 5. Angular momentum and spin
· Representation of the rotation group : U^_1 V U = R V
· Irreducible representation : j and m
· Consistent algebra : half-integer and integer j
· Orbital angular momentum and spin angular momentum
· SO(3) to SU(2)
· SO(1,3) homeomorphic to SU(2) \times SU(2)
· Non-relativistic SO(3) : diagonal SU(2) of SU(2) \times SU(2)
· Angular momentum addition
· Tensor operators
Lec 6. First quantization and second quantization
· 1st quantization : X and P as an operator, [X, P] = it as a label
· 2nd quantization : relativistic (t,x) equally as a label "Relativistic quantum mechanics = Quantum Field Theory" \Psi as an operator and (t,x) as a label
· Creation and/or annihilation of a particle at (t,x)
· Spin-statistics theorem : [\Psi, P_\Psi]=i or {\Psi, P_\Psi}=i
